The most crucial means of understanding one another is communication. However, our messaging style can change depending on the situation we find ourselves in.
What if you were a part of the aviation sector? What would happen if you were mid-flight? How are you going to convey information most clearly and simply?
When it comes to aviation, communicating can take on various forms. It’s not the normal exchange of information between students and teachers.
Airport Communications as a First-class Solution
A digital radio network facilitates better security and flight management. With proper airport communication systems, passengers are aware of their safety. Thus, the quantity of people traveling by air is increasing. The amount of freight carried is also growing.
The issues of energy, wages, competition, and safety are only getting worse. Digital radio communications in this sector support airport operations in several ways, including:
- Streamline Operations
Adding to the complexities:
- Number of Communications
There’s no need for any other facilities to link this many individuals in such a small geographic area. You can fulfill all of these demands with the use of an adaptable digital radio communication system.
- Geographic Scope
The facilities at a major aviation typically span between thirty and forty kilometers. Everywhere can receive radio coverage through a radio network. This covers hangars for repairing aircraft, luggage or cargo facilities, and subterranean parking lots.
- Diverse Groups
The following user groups are common at airports:
- Airlines
- Security Personnel
- Tower and Apron Control
- Emergency and Rescue
- Ground Handling
- Catering
VPNs aid in meeting the intricate radio communication requirements of airports. It preserves the privacy of certain groups while providing limitless voice and message interactions.
- Manage Flights
Hundreds of flights are handled daily by crowded airports. Each necessitated an exchange of information between dozens of workers. Some workers only work on one aircraft at a time, such as loadmasters and handle baggage – read https://www.iata.org/en/programs/ops-infra/baggage/rfid/ to learn more. Some serve multiple flights, such as ramp agents.
Using a radio network, the dispatchers can establish virtual discussion groups for every aircraft from a distance. Dispatchers organize all flight attendants into a discussion group. By just pressing the push-to-talk button, members can communicate with one another.
An individual handling many flights can monitor conversations within each of her groups. He can accomplish this by using his radio’s priority-scanning capability.
- Save money
If a protected radio network fails, the other one instantly takes over. Redundancy ensures dependable, always-on dispatch operations. Reduced maintenance and repair expenses are another benefit of increased reliability.
- Improve security
Modern security systems were incorporated throughout the network. The business has gained recognition for its security advancements on a global scale as a result.
It enables you to promptly notify every employee if there’s an emergency. It provides dozens of security elements to assist in meeting their security requirements. This includes terminal/network authentication, emergency calls, air interface, and end-to-end encryption.
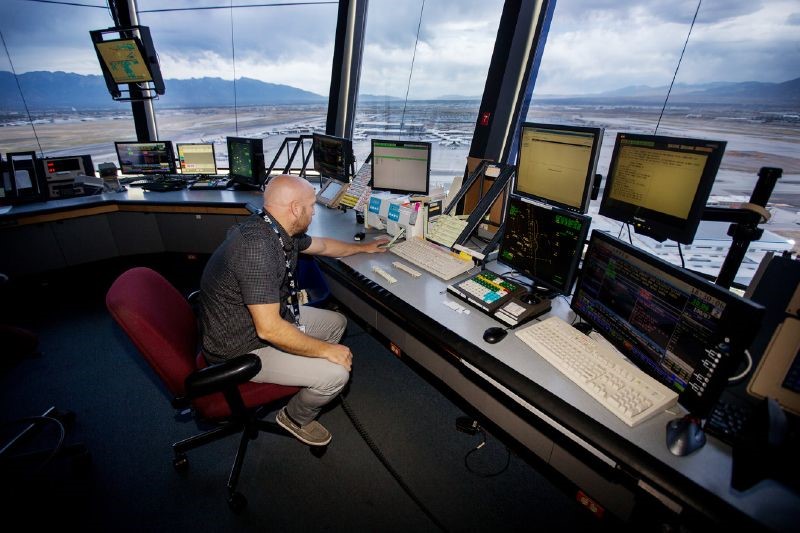

Types of Airport Communication Systems
Communication guarantees the effectiveness, seamlessness, and safety of activities. Find out more about the various security networks and systems. They’re essential to the messaging methods used by airports.
- Voice Communication Control Systems
Employees can communicate with a variety of aircraft and airports by using a VCCS. It makes use of a decentralized system hosted in the cloud. When needed, this interprets speech data and sends it to the appropriate aircraft.
Among the duties are the following:
- notifying and informing pilots of other aircraft or potentially dangerous situations
- granting permission for takeoff and landing
- giving traffic control centers command over departing flights
An airport that has a VCCS in position is completely in control of who it communicates with. It’s greatly simplifying continuous statements across congested skies.
- Air-to-Ground
This guarantees that pilots notify airports of any problems with the aircraft or the passengers within. This indicates that the pilot and the airport may collaborate closely. They’re able to organize a fix for any persistent issues.
For example, preparing ground paramedics or performing an emergency landing. The most crucial aspect of managing an airport is safety. Maintaining a steady line of communication between pilots and controllers guarantees everyone’s safety.
- UHF/VHF
It’s Ultra-High and Very High-Frequency radio communications – look at this for added info. This sends audio to the ground and via the air via a high-frequency signal. These systems’ ranges are extremely diverse.
The power used by various airports varies. With radios that can transmit signals across hundreds of miles. By using a system of this kind, communication is guaranteed to be dependable and transparent.
- Compliance and Legal Recording Systems
Any airport’s ability to operate successfully depends on its ability to communicate. Authorities must launch inquiries as soon as it’s practical after something goes wrong. Thus, it’s imperative to have thorough compliance and legal documentation systems.
Airports and airplanes continuously record their communications. The airport can prove it satisfies the requirements in the event of an audit. Finishing the conversation is a crucial step in the procedure. However, recording is equally necessary to ensure quality.
- Human-Machine and Machine-Machine
Also known as Automation, it reduces human error. That’s the moment when the pilot issues commands to the device. That message is sent to additional computers.
Routine actions are less likely to result in pilot error when they are automated. granting them the benefit of enabling them to concentrate on more challenging assignments. It also gives their responsibilities a managerial component.
These concepts, which are also known as human-centered automation, are as follows:
- Premise
The safety of the flight is exclusively a pilot’s responsibility. The controller is in charge of ensuring safe flow and separation of traffic.
- Axiom
Pilots have to maintain control over their aircraft. Air traffic control must stay in the hands of controllers.
- Corollaries
Both the pilot and the controller need to be capable of monitoring the automation, actively involved, and well-informed. As a result, the automated systems need to be dependable and keep an eye on the human operators. Every intelligent component of the system has to be aware of one another’s intentions.